"Decode SDS: Everything You Need to Know to Stay Safe with Chemicals"

If you work with chemicals, it is essential to know how to read a Safety Data Sheet (SDS). The SDS provides information about the potential hazards of a chemical substance & how to handle it safely. In this blog post, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to read & interpret an SDS.

Outlines or Map of the following Blog:
- What is an SDS?
- The Importance of SDS.
- How to Read an SDS.
- Section 1: Identification.
- Section 2: Hazard(s) Identification.
- Section 3: Composition/Information on Ingredients.
- Section 4: First-Aid Measures.
- Section 5: Fire-Fighting Measures.
- Section 6: Accidental Release Measures.
- Section 7: Handling and Storage.
- Section 8: Exposure Controls/Personal Protection.
- Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties.
- Section 10: Stability and Reactivity.
- Section 11: Toxicological Information.
- Section 12: Ecological Information.
- Section 13: Disposal Considerations.
- Section 14: Transport Information.
- Section 15: Regulatory Information.
- Section 16: Other Information.
- Conclusion.
- FAQs.
What is an SDS?
An essential document for workplace safety regarding hazardous chemical substances is the Safety Data Sheet (SDS). It contains comprehensive information about the potential hazards associated with a chemical & provides instructions on how to handle and store it safely. SDSs are often required by law in most countries and are commonly provided by the manufacturer or supplier of the chemical.

The Importance of SDS
The primary purpose of an SDS is to ensure that individuals who work with or are exposed to hazardous chemicals are aware of the potential risks & how to handle them safely. SDSs are a vital component of any chemical safety program & should be readily available in the workplace for easy access. Employers should also provide appropriate training to their employees on how to read & interpret SDSs to ensure their safety & well-being.

How to Read an SDS
Reading an SDS can be overwhelming initially, but breaking it down into sections can make it easier to understand. The following sections are typically included in an SDS:
- Section 1: Identification:
This section provides information about the chemical substance, including its name, manufacturer/supplier information, & recommended use. It also includes emergency contact information for the supplier.

- Section 2: Hazard(s) Identification:
This section identifies the potential hazards of the chemical substance, including physical & health hazards. It also provides information on the degree of each hazard & any precautions that should be taken.

- Section 3: Composition/Information on Ingredients:
This section lists the ingredients in the chemical substance & their concentration levels. It also includes any impurities & stabilizing additives.

- Section 4: First-Aid Measures:
This section provides instructions on what to do if someone is exposed to the chemical substance, including the appropriate first-aid measures to take.

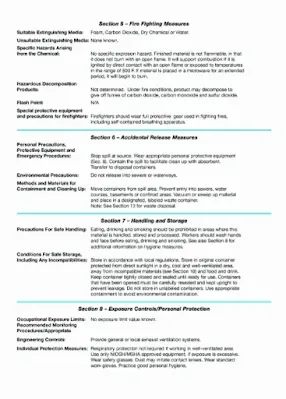
- Section 5: Fire-Fighting Measures:
This section provides information on how to extinguish a fire involving a chemical substance safely. It also includes any special firefighting procedures or protective equipment that should be used.
.webp)
- Section 6: Accidental Release Measures:
This section provides instructions on how to respond in the event of a spill or release of the chemical substance. It includes information on containment, cleanup, and disposal.

- Section 7: Handling and Storage:
This section provides instructions on how to handle & store the chemical substance safely. It includes information on proper ventilation, temperature, and other storage conditions. The section may also provide information on any incompatible substances or materials to avoid, as well as recommendations for handling & transporting the substance safely.
.webp)
- Section 8: Exposure Controls/Personal Protection:
This section provides information on how to control exposure to the chemical substance and protect oneself from potential hazards. It includes recommendations for personal protective equipment, such as gloves, respirators, and eye protection.
.webp)
- Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties
This section provides information on the physical & chemical properties of the chemical substance, such as boiling point, melting point, and pH. It also includes information on the substance's appearance, odor, and other relevant characteristics.
.webp)
- Section 10: Stability and Reactivity:
This section provides information on the stability & reactivity of the chemical substance. It includes information on any hazardous reactions that may occur when the substance is exposed to heat, light, or other chemicals.
.webp)
- Section 11: Toxicological Information:
This section provides information on the toxicological properties of the chemical substance, including its acute & chronic effects on human health. It includes information on the substance's potential to cause cancer, genetic mutations, and other adverse health effects.
.webp)
- Section 12: Ecological Information:
This section provides information on the potential impact of the chemical substance on the environment, including its potential to harm aquatic life, vegetation, & wildlife. It includes information on the substance's biodegradability & potential for bioaccumulation.

- Section 13: Disposal Considerations:
This section provides information on how to dispose of the chemical substance safely, including any regulatory requirements for disposal. It includes information on any special precautions that should be taken when disposing of the substance.

- Section 14: Transport Information:
This section provides information on how to transport the chemical substance safely, including any regulatory requirements for transport. It includes information on any special precautions that should be taken when transporting the substance.
.webp)
- Section 15: Regulatory Information:
This section provides information on any regulatory requirements for the chemical substance, including any restrictions on its use or disposal. It includes information on any applicable regulations, such as OSHA, EPA, and DOT.
.webp)
- Section 16: Other Information:
This section provides any additional information that may be relevant to the safe handling & use of the chemical substance, such as information on storage & handling.
-min.webp)
Conclusion
Reading & understanding a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is essential for anyone who works with hazardous chemicals. By breaking the SDS down into sections & understanding what each section contains, individuals can ensure that they are handling & using the chemical substance safely & effectively.
-min.webp)
FAQs
Q: What is a Safety Data Sheet (SDS)?
A: An SDS, also known as a Safety Data Sheet, is a document that provides thorough information about a hazardous chemical substance.
Q: Why is it essential to know how to read an SDS?
A: Having the ability to read an SDS is essential to ensure that individuals who handle or are exposed to hazardous chemicals are fully aware of the potential risks & know how to handle them safely.
Q: Who typically provides SDSs?
A: SDSs are typically provided by the manufacturer or supplier of the chemical substance.
Q: What information is included in an SDS?
A: An SDS typically includes information about the chemical substance's potential hazards, composition, first-aid measures, fire-fighting measures, accidental release measures, handling & storage instructions, exposure controls/personal protection, physical & chemical properties, stability & reactivity, toxicological information, ecological information, disposal considerations, transport information, regulatory information, and other relevant information.
Q: What is the purpose of an SDS?
A: The primary purpose of an SDS is to ensure that individuals who work with or are exposed to hazardous chemicals are aware of the potential risks & how to handle them safely.

Q: How often should SDSs be updated?
A: SDSs should be updated whenever new information becomes available or when changes are made to the chemical substance.
Q: Are SDSs required by law?
A: Yes, SDSs are required by law in many countries, including the United States.
Q: Can SDSs be stored electronically?
A: Yes, SDSs can be stored electronically as long as they are easily accessible & up-to-date.
Q: Who is responsible for providing SDSs to employees?
A: Employers are responsible for providing SDSs to their employees who work with hazardous chemicals.
Q: Can SDSs be written in languages other than English?
A: Yes, SDSs can be written in languages other than English if the employees who work with the chemical substance are more comfortable with another language.

Q: Can SDSs be used for different chemical substances?
A: No, SDSs are specific to the chemical substance they describe & should not be used for other substances.
Q: Do SDSs provide information about first-aid measures?
A: Yes, SDSs typically include information about first-aid measures in case of exposure or accidental ingestion.
Q: What is the difference between an SDS and a label?
A: An SDS provides comprehensive information about a hazardous chemical substance, while a label provides basic information about the substance, such as its name, hazard warning, & precautionary measures.
Q: Are SDSs only required for industrial chemicals?
A: No, SDSs are required for all hazardous chemicals, including those used in consumer products.
Q: How can employees access SDSs?
A: Employers should provide employees with access to SDSs either in paper form or electronically.

Q: Are SDSs the same as Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs)?
A: Yes, SDSs are the updated version of MSDSs, which were used before the implementation of the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification & Labeling of Chemicals.
Q: How can employees be trained to read SDSs?
A: Employers should provide training to employees on how to read & understand SDSs, including information on the different sections & what they contain.
Q: Can SDSs be used as a substitute for hazard communication training?
A: No, SDSs should be used as a supplement to hazard communication training, but they should not be used as a substitute for it.
Q: Are SDSs required for non-hazardous chemicals?
A: No, SDSs are only required for hazardous chemicals that meet certain criteria.
Q: Can SDSs be used to determine the toxicity of a chemical substance?
A: Yes, SDSs can provide information about the toxicological properties of a chemical substance & its potential to cause adverse health effects. However, it is important to note that SDSs should not be used as the sole source of information when assessing the toxicity of a substance.



